Personality comes from the cognitive, emotional, and behavioral characteristics we possess and influences all of our interactions and, ultimately, how we engage with the world on a daily or ongoing basis.
In a working situation, it can determine not only people’s work preferences, communication styles, and collaboration, but also whether an individual thrives and to what extent of their full potential they work.
Carl Jung’s psychological theory provides a larger foundation for these differences, whereby he proposed there are four key psychological functions of people: thinking, feeling, sensation, and intuition. He also proposed two generalized attitudes: introversion and extraversion. These dimensions form the basis of Jungian archetypes, which categorize people into distinct personality patterns.
Jung’s insights paved the way for modern personality frameworks, including the widely used Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI). By exploring personality types through Jung’s lens, we can better understand how different individuals function in the workplace to foster a more productive and harmonious work environment.
Table of Contents
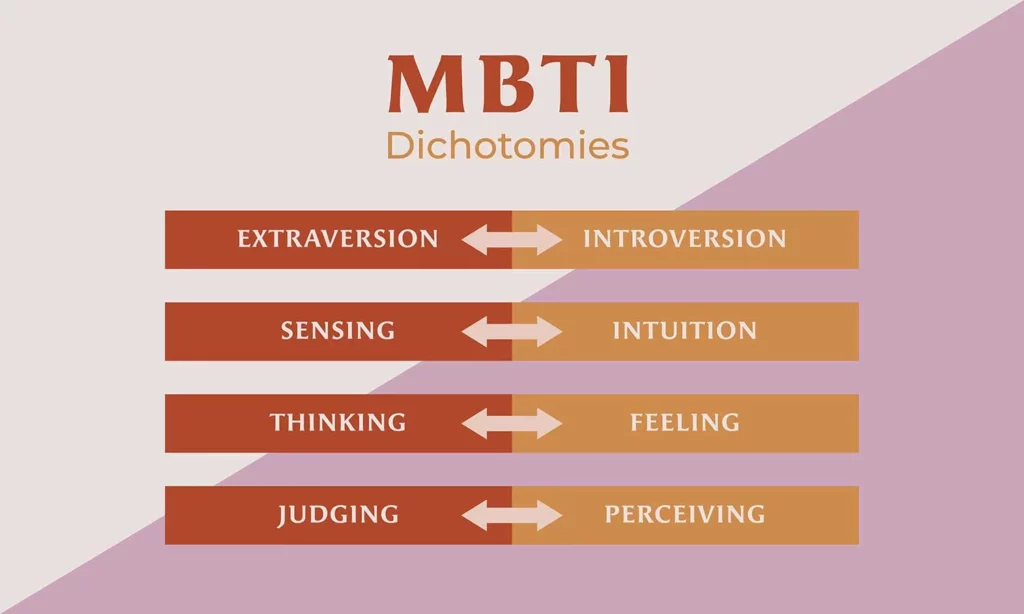
The Four Dichotomies
There are four major dichotomies that shape personality types; they help to explain how individuals interact with the world, how they process information, and how they make decisions. These dimensions can help delineate different personality characteristics and workplace behavior.
Extraversion (E) vs. Introversion (I)
According to Jung, this dimension refers to an individual’s orientation to the world. Introverts are internally focused, where they feel comfortable with isolation and engagement in their own thoughts. Extraverts are externally focused, where they are comfortable in social environments to engage with others.
Sensing (S) vs. Intuition (N)
This dimension refers to how an individual processes information. Sensing types rely on concrete reality and their senses to explore, examine, and analyze parts of that reality. Intuitive types are interested in possibilities, trends, and abstract analysis.
Thinking (T) vs. Feeling (F)
This dimension is how people make decisions based on what they have learned. Thinkers emphasize logic, facts, and impartial reasoning; feelers take into account feelings, values, and how their decision will impact others.

Judging (J) vs. Perceiving (P)
This dimension is how people deal with the outside world. Judging types prefer structure, organization, and firmness in decisions; perceiving types are flexible, spontaneous, and open to change.
Together, these four dimensions create 16 personality types, identified by four letters. According to the MBTI, a person’s type remains relatively constant over time. This will affect their preferences in the workplace, what they are good at, and how they deal with others.
Personality Types and The Workplace
Here you can read about how the different types engage with work, decisions, and teamwork.
The E-Types
Here are the known E-types:
ESTP
An ESTP is vibrant, lively, outgoing, and somewhat spontaneous. They live for the moment and thrive on risk while also being very pragmatic individuals. ESTPs are adaptable; decisions are made quickly, and they act. DESTPs can act quickly, and because they don’t consider long-term plans/actions, they can react without considering future consequences.
In the workplace, ESTPs will be more successful in fast-paced environments like sales, marketing, and emergency work, where their enthusiasm and charm will impress and help them excel.
ESFP
ESFPs are exciting, energetic, and fun people who love socialization and entertainment. They bring excitement and positivity to the workplace and inspire others to feel good in a team environment. ESFPs are good people; they have excellent interpersonal skills, they can easily adapt to situations, and they are also very optimistic, which supports the idea of teamwork and interpersonal connection. It could become difficult for them to plan for the long term, as they tend to also run with diversions.
ESFPs will excel in social careers with dynamism, like sales, hospitality, or entertainment; their adaptability and charm will fit well in those environments.
ENFP
ENFPs are imaginative and enthusiastic individuals driven by a desire to form deep connections. They flourish in creative and people-oriented roles, blending innovation with strong interpersonal skills. Their ability to inspire and communicate effectively makes them great motivators. Yet, their excitement and tendency to juggle multiple ideas at once can sometimes make it difficult for them to maintain focus.
ENFPs thrive in flexible, innovative workplaces such as public relations and marketing, where they can explore fresh ideas and engage with others.
ENTP
ENTPs are curious and outspoken individuals who love debating ideas and exploring new possibilities. They challenge conventional thinking and promote innovation through their strategic and problem-solving abilities. Strong communication, analytical thinking, and creativity are among their strengths. Their inclination to argue and overlook finer details may, at times, lead to conflicts or missed nuances.
ENTPs perform best in intellectually stimulating roles such as consulting, law, and entrepreneurship, where strategic planning and debate are valued.
ESTJ
ESTJs are organized, assertive, and pragmatic. They value efficiency and tradition. They value continuity and efficiency in their lives. They face the world with a sense of process and order. In group settings, they often take stronger roles so that work is completed efficiently and effectively. Their leadership, their efficiency, and their decisiveness make them strong managers of group work. However, their high need for order and structured direct feedback can be perceived as inflexibility, and this can be negatively impactful on team dynamics and team morale depending on choices made.
ESTJs are energized in structured environments where results matter, like management, operations, and law enforcement, where organization and leadership skills are needed to be successful.
EFSJ
ESFJs are warm, cooperative, and empathetic individuals who value harmony and enjoy helping others. They like working in teams, and they have great skills creating safe, supportive, and welcoming environments for other people to prosper in. An abundance of caring drives them, and sometimes that can make it difficult to adapt to big shifts in circumstances.
ESFJs thrive in collaborative environments that value people’s organizational skills, empathy, and people skills, whereby caring for people and the greater good are valued. These roles can include human resources, teaching, and health care, where all three of the above skills are valued.
ENFJ
ENFJs are compassionate, sociable, and altruistic individuals who are driven by a desire to lead with purpose and support others. They succeed in leadership positions when they utilize their great skills in interaction, using their interpersonal skills to create positive and uplifting environments. They may find that their idealism and openness to opinions and feedback can undermine their ability to accept setbacks when they occur.
When it comes to occupations for ENFJs, coaching, leadership, and teaching positions seem to fit with their desire to support and inspire others while also developing community.
ENTJ
ENTJs are bold, strategic, and decisive individuals. They prioritize efficiency and future initiatives. ENTJs want to lead through decisions, structures, and futures. However, while they are very effective leaders, they can be direct and dominating, and that comes across as aggressive or dismissive of other people’s perspectives. They thrive in executive leadership, business strategy, and project management positions.
The I-Types
ISTJ
ISTJs are practical, meticulous, and responsible people who value loyalty and traditions. They prefer to follow a structure with known rationale because it is reliable and they can get work done accurately. ISTJs are very reliable and detailed workers, and they are the members of a team who you can rely on to get things done. However, ISTJs are not flexible when it comes to work, and although they follow the rules, they can be rigid and criticize those who do not follow the rules.
ISTJs are best in structured environments with expectations outlined beforehand. ISTJs excel in administrative roles and project management.
ISFJ
ISFJs are nurturing, diligent, and cooperative, excelling in roles that allow them to support others. They are very organized and prefer situations where responsibilities are clearly defined. Their persuasive nature and gift for facilitating teamwork and cooperation allow them to help groups work together in harmony. However, ISFJs can struggle to assert their own needs and adapt to sudden changes.
ISFJs can thrive in jobs like teaching, medical fields, or customer service – where people depend on their attentiveness and sense of duty.
INFJ
Deeply intuitive and idealistic, INFJs are driven by a desire to create positive change. They seek meaningful work that aligns with their values and allows them to guide and inspire others. Their ability to connect deeply with people and think strategically makes them powerful motivators. On the downside, their perfectionism and sensitivity can lead to stress, and they may become overwhelmed by high emotional demands.

INFJs flourish in counseling, social work, and strategic planning, where their vision and empathy are most effective.
INTJs
INTJs are logical, strategic, and forward-thinking, excelling in roles that require problem-solving and innovation.
They have an ability to create long-term goals and develop appropriate solutions. They have a strong preference for efficiency and are most able to thrive with freedom and intellectual challenges. Although their independence and personal accountability are definitely assets, they may have difficulty expressing emotions and face frustration and disappointment in teamwork when others do not have the same drive for excellence.
ISTP
ISTPs are hands-on, adaptable, and highly analytical, excelling in environments that demand quick thinking and technical expertise. They excel in situations where their practical problem-solving ability and self-management skills are required in a fast-paced working environment. Their ability to stay calm in chaotic situations means they thrive in a work environment that is exciting and intense and where every day will be different. However, they do not like routine and fairly monotonous work tasks, nor do they easily make long-term commitments.
ISTPs can apply their technical skills and be engaged in dynamic tasks in engineering, info-tech, and skilled trades.
ISFP
Creative and spontaneous, ISFPs bring artistic insight and emotional depth to their work. They appreciate roles that encourage self-expression and versatility – often performing very well in fields that are visually or emotionally oriented. They are detail-oriented and adaptable team members in ever-changing landscapes, but their fear of conflict and difficulty with assertiveness can sometimes keep them from asserting themselves.
ISFPs often flourish in careers in design, art, and healthcare, where their sensitive nature and creativity add dimension to their work.
INFP
INFPs are idealistic, imaginative, and deeply empathetic, seeking work that aligns with their values and allows them to make a difference. They are distinguished by their commitment to meaningful work and creative expression. They’re self-reflective and ideal in a role that allows their personal development and independence, but practical challenges may become overwhelming, and they could become withdrawn if they are working in structured environments.
Writing, counseling, or non-profit work gives INFPs the ethical and creative dimension they seek.
INTP
They are open-minded and exploratory and enjoy challenging intellectual work with theories and constructs outside of everyday experience. They thrive in a workplace requiring deep work/independent analysis as they seek alternative solutions to a given problem. INTPs are served by their logic and problem-solving ability and have an important role in research-driven work. Social relationships may be hard and predictable due to criticism diminishing feelings because it can be detached and self-reobservant.
Research, IT, and academia are where INTPs thrive in independent work and research-intense areas requiring analytical depth!
Your Work, Your Way
Using personality type information in the employment setting will allow the organization to have improved workplace team development. Understanding the individual preferences that employees have each day allows organizations to establish hiring and retention practices.
Using personality type models like MBTI allows HR practitioners to establish a workplace that encourages diversity and inclusion, is supportive of its employees, cultivates engagement, and enables employees to contribute to overall organizational success in a manner that aligns with their preferences. This creates a productive workplace environment while supporting a culture that does well.
Have a great idea? Let EvolveDash bring it to life! We specialize in empowering businesses with innovative digital solutions. We create custom mobile apps and build user-friendly websites, providing tailored solutions to meet your needs.
With over 100 satisfied clients and 450 successful projects, our team has the expertise needed to help your business stand out in a competitive market. Reach out to us today!
FAQs
Can personality types change over time?
While personality preferences are generally stable, they can evolve due to personal growth, life experiences, or new environments. The MBTI reflects current preferences rather than fixed traits.
How do personality types influence workplace behavior?
Personality types affect how individuals communicate, make decisions, handle stress, and interact with colleagues. Understanding these traits can help create more effective teams and improve workplace collaboration.
Can understanding personality types improve team dynamics?
Yes, recognizing different personality types helps managers align team members with complementary skills, fostering better collaboration, communication, and conflict resolution.
Can knowing my personality type improve my career?
Yes, understanding your personality type can help you align your career choices with your strengths, improve your communication skills, and enhance your overall work experience.
Is the MBTI scientifically validated?
The MBTI has been widely used and supported in various professional settings, but it has received some criticism regarding its scientific reliability. Despite this, many organizations still find it valuable for improving interpersonal relations and team collaboration.



















