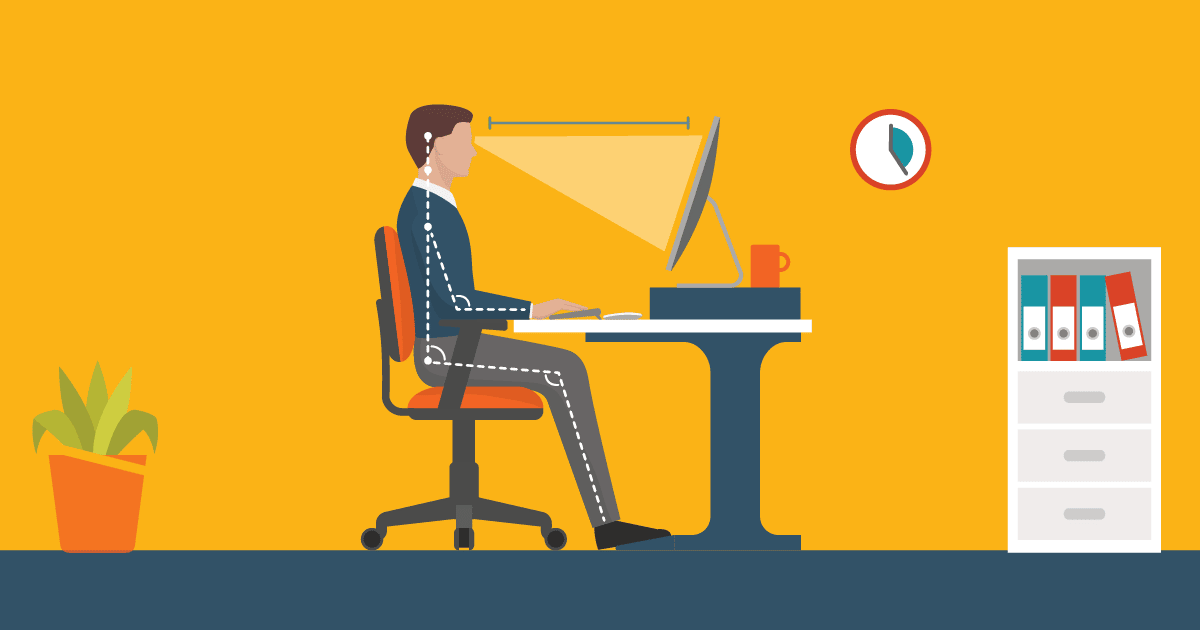
How to Improve Your Posture At Work
Good posture is more than just sitting up straight! It is about aligning your body in a way to minimize strain on your muscles, joints, and spine. Most of us spend hours at a desk and in front of screens during working hours. Proper body posture is critical to avoid discomfort, pain, and ultimately long-term health repercussions.
On the other hand, poor posture can affect not only your body but also your productivity, mood, and energy for the day. The good news is that it is possible to create better posture and lessen your chances of injury with a few new habits and exercises.
In this article we will discuss how to incorporate good posture at work and into your life in a practical and effective way.
Table of Contents
What is Posture?
Posture refers to the natural way your body holds itself while sitting or moving. Maintaining your posture relies greatly on your musculoskeletal system.
Muscles, ligaments, tendons, and joints actively control and adjust your position so that you stay stable and comfortable. For instance, when you are in a seated position, your body is able to maintain a posture so you do not slide out of the chair.
Posture allows you to move by facilitating shape change in your body shape. Without this shape-change ability, basic movements like bending down to pick something up would be very difficult because you could not change your body shape to perform the movement.
There are two different forms of posture: static and dynamic posture. Static posture is how your body holds itself in a stationary position, like sitting, standing, or lying. Dynamic posture is how your body maintains stability while in motion, like walking, running, or reaching.
Why Posture Matters
In the current work environment, improper posture is one of the largest determinants in predicting overall health outcomes. Inappropriate alignment with both sitting and standing can cause misalignment of joints, strain on muscles, or extra pressure on the spine.
Over time, all of these can lead to detrimental chronic back pain, discomfort, and potentially irreversible damage to your health. Research studies have shown that regardless of one’s activity levels, if you work and sit for long periods of time in poor postures, the risk of developing musculoskeletal disorders like osteoarthritis and chronic disease can gradually increase over time.
When postural habits are unaddressed, various adversities can occur, including:
- Poor joint alignment causing discomfort and pain
- Poor positioning leading to muscle soreness from the extra strain placed on them
- Increased pressure on the spine which can interfere with disc structures and potentially lead to long-lasting damage
- Compression of disc and joint structures that could limit movement, and lead to pain
- Reduced space for nerves, that can cause nerve entrapment that could lead to pain or discomfort
- Reduced blood flow in the body, which can lead to fatigue, lethargy and lower energy levels
- Overuse injuries from repetitive movement sequences produced from bad posture habits
Posture issues, like Upper Cross Syndrome and Lower Cross Syndrome, are a common occurrence in the workplace, but they happen anywhere that people sit or stand for long periods of time.
Upper Cross Syndrome occurs when you sustain poor sitting posture by having your head forward, which leads to rounded shoulders and an arched upper back. When our body is in poor athletic posture, usually standing, this will cause the pelvis or hips to seem forward when absorbed, which leads to an arched lower back. This can lead to pain in the lower back and legs.
Regularly practicing good posture can help you feel better physically and mentally, leading to increased productivity and reduced stress levels.
The following are some main benefits of good posture:
- Better bones and joints, reduces the chances of sustaining long-term injuries
- Increased productivity by improving blood flow to the muscles
- Improved mood and having a more positive outlook by having less physical discomfort
- Decreased pressure on vertebrae, which leads to less back pain/discomfort
- Reduced chances of on-the-job injuries. Good posture promotes balance and alignment
Integrating good posture into your daily routine can reduce a variety of health issues while encouraging productivity/overall well-being.
What Causes Bad Posture
Musculoskeletal pain that happens due to desk work can be attributed to multiple factors. The most significant factor that creates issues is slouching postures that occur in seated postures. Slouching can lead to the spinal structure being not aligned, creating tension and stretch across structures, which leads to discomfort.
Another significant factor is poor workstation setup. If the monitors you are working with are not set up at eye level, it will put unnecessary strain on your neck and shoulders and lead to discomfort. Additionally, poor habits, like crossing your legs or your ankles, can over time create misalignment of your hips, lead to discomfort in your lower back and even your hips.
Moreover, lack of movement throughout the day is a contributor to musculoskeletal pain. Sitting too long puts a damper on blood flow (nutrient flow) to your spinal discs, which are critical for providing cushioning and protection to your spine.
Over time, excessive amounts of sitting can inhibit the “against” movement of the spinal discs, leading to degeneration and increased chances of acquiring chronic conditions (chronic back pain) and other musculoskeletal disorders. Ensuring that you are moving adequately (proper ergonomics) is critical in preventing these issues.
Ways to Improve Your Posture at Work
We’ve put together a variety of tips and practices to help you achieve good posture and leave health issues behind.
Stretching Exercises
Stretching is a key to maintaining flexibility and relieving tightness resulting from poor posture. Stretching elongates shortened muscles and helps combat the effects of prolonged sitting or standing in one position.
Stretching not only helps reduce discomfort but also improves overall posture. When stretching, we must be cautious not to overstretch, or we may injure ourselves. Stretching not only helps reduce discomfort but also improves overall posture.
Typing, texting, and endless mouse clicking can leave your wrists and shoulders feeling tight. Practice the following stretches to give yourself some relief.
For your wrists:
- Extend your arms in front of you, forming fists with both hands.
- Slowly rotate your wrists outward in a circular motion, then inward.
This movement helps improve blood circulation to your hands, reducing stiffness and promoting flexibility.
For your shoulders:
- Reach your arms straight out and interlace your fingers.
- Turn your palms outward.
- Slowly raise your arms overhead and feel the stretch.
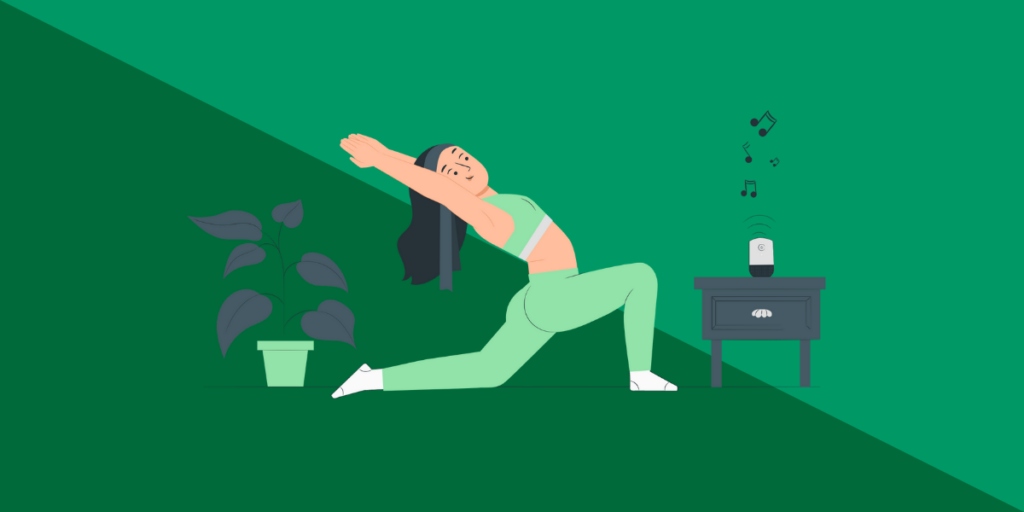

If you’ve been sitting for a while, this stretch will help release tension in your upper back:
- Sit comfortably in your chair and cross your arms in front of your chest.
- Keep your lower back steady, and gently lean back to arch your upper back as far as it feels good.
- Hold for 10 seconds.
- Repeat 3 times.
Open up your chest and reverse that hunched posture with this stretch:
- Place your forearm against a door frame, keeping your elbow bent at 90º.
- Slowly rotate your body away from the door until you feel a comfortable stretch.
- Hold for 30 seconds.
- Repeat 3 times on each side.
Strength Exercises
Strength exercises are an important component of posture support and muscular fatigue. These exercises focus on the muscles that help hold up your spine and posture to improve balance, stability, and alignment. It is widely accepted that strength exercises addressing muscle groups such as your core, shoulders, hips, and legs are an excellent way to help improve weak parts of your body that could develop pain or discomfort.
Core exercises like planks or bridges strengthen the muscles that help keep your spine stable, whereas shoulder or leg exercises will work to assist you to maintain posture while reducing the chances of slumping or having shoulders and legs out of alignment. For optimal results, it is suggested to incorporate strengthening exercises into your routine a minimum of 2 to 3 days a week.
Regular Movement
No single posture is ideal for long periods of time. It’s important to understand that even with an ergonomic setup, being in a static position will cause discomfort and stiffness. For this reason, it’s very important to check your posture frequently, ideally every 15 minutes, and take breaks every half hour to move around.
Regular movement will avoid excess muscle strain and induce better blood circulation. Standing, walking, or stretching are simple things to do frequently to keep your body feeling good throughout the workday.
Neck Position
Your neck position plays a critical role in overall posture and spine health. Straining to see a computer monitor that is too close or far away, or twisting your neck to use dual screens, can lead to neck, back, and shoulder strain.
To improve neck alignment, raise your chair so your eyes are level with the top of the screen. If you’re using a laptop, connect it to a larger monitor and use your swivel chair to adjust the view, rather than straining your neck. Keep essential tools like your mouse and headset within easy reach to avoid unnecessary stretching.
Ergonomics
Creating an ergonomic workspace is one of the easiest and most effective ways to improve posture and reduce the risk of workplace injury. A properly set-up desk, including an ergonomic chair that supports the spine, is essential.
Simple adjustments, such as keeping your monitor at eye level, ensuring a 90-120 degree angle for your wrists, and sitting with your back against the chair, can make a big difference. Engaging an ergonomic specialist to assess your workspace and provide training on correct posture techniques can help make your workplace safer and more comfortable.
Standing Desks
Standing desks have become more popular in the last few years, thanks to studies that concluded differences in health and productivity related to prolonged sitting. Standing for a portion of the day has proven to reduce the compressive forces on the spine and body from long sitting sessions.
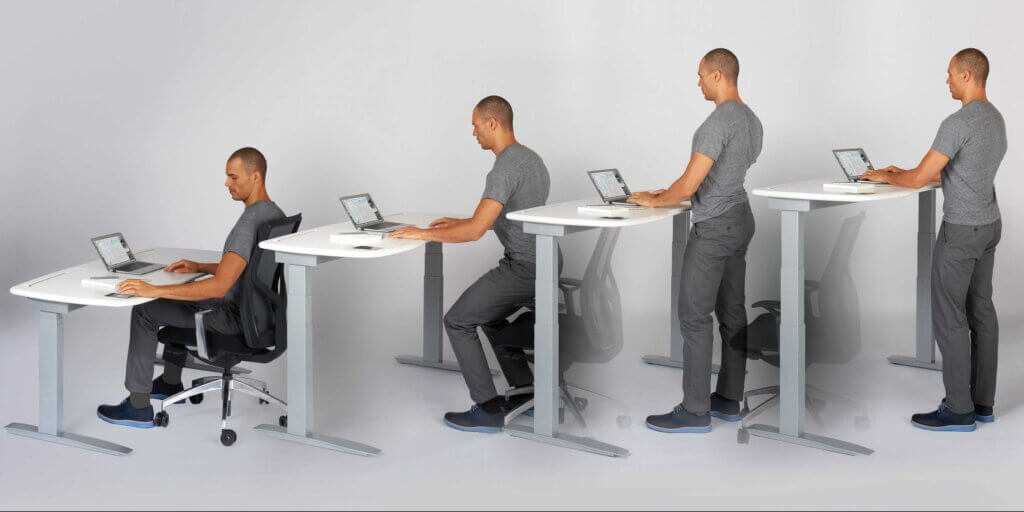

These desks also establish a more neutral spine position and encourage movement. To correctly use a standing desk, follow the 20:8:2 rule: 20 minutes of sitting, 8 minutes of standing, and 2 minutes of movement. Regular reminders to adjust posture can ensure better usage and reduce strain on the body.
While Lying Down
Good posture doesn’t stop when you’re off the clock. It’s essential to maintain proper posture even when lying down to prevent back pain and muscle strain. When getting in and out of bed, use techniques like bending your knees and rolling to your side before sitting up. These small steps protect the spine and reduce the risk of injury during transitions from lying to sitting positions.
Small Steps, Big Gains
Maintaining good posture at work is essential for preventing pain, improving productivity, and supporting long-term health. Small changes like ergonomic adjustments, regular movement, and targeted exercises can make a big difference. By being mindful of your posture and making proactive changes, you can reduce strain on your muscles and joints, enhancing comfort and efficiency.
Looking for more ways to enhance your workplace and lifestyle? Explore our blogs on EvolveDash for fresh insights and practical tips on improving efficiency, comfort, and overall well-being!
FAQs
Why is good posture important at work?
Good posture reduces strain on muscles and joints, preventing pain, fatigue, and long-term health issues. It also enhances focus and productivity.
How can I improve my posture while sitting?
Keep your feet flat, sit with a straight back, and position your monitor at eye level. Adjust your chair to support your lower back.
How often should I take breaks to prevent posture issues?
Take a break every 30 minutes to stretch, walk, or adjust your position to prevent stiffness and strain.
Can bad posture cause long-term health problems?
Yes, prolonged poor posture can lead to chronic pain, joint problems, and musculoskeletal disorders over time.
What are some simple exercises to improve posture?
Try stretching, core strengthening, and shoulder rolls to relieve tension and build muscle support for better posture.



















