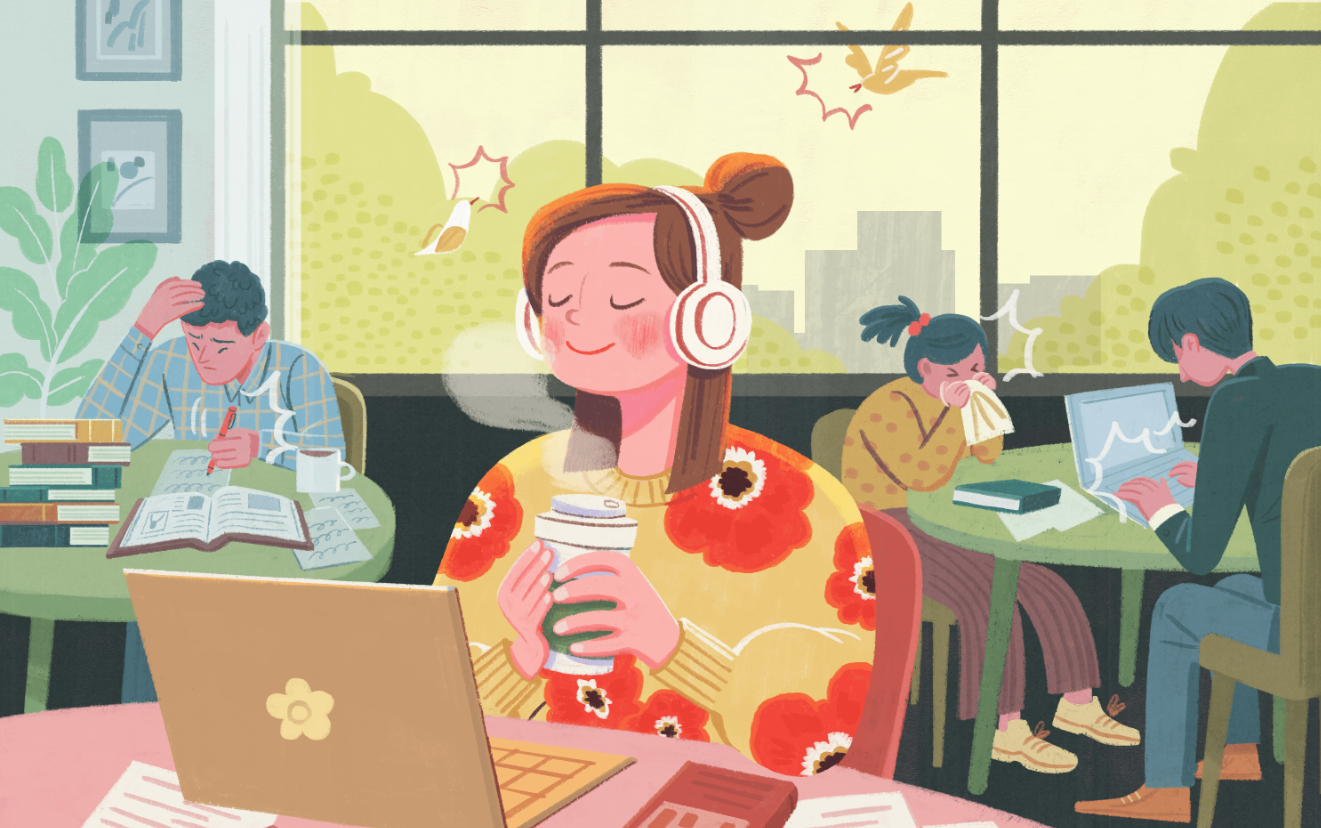
Misophonia is a condition whereby people have extreme dislike or anger towards some sounds or stimuli, such as tapping, ticking, or chewing. While mild irritation with these sounds, even if highly annoying for most, is experienced by others, the suffering misophonia experiences can negatively affect their daily lives or even stop them from functioning in society. For people who experience misophonia, some form of treatment is required to help manage their symptoms and triggers.
Misophonia is also known as Selective Sound Sensitivity Syndrome. It originated from a Greek term that translates to “hatred of sound.” Misophonia is not in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 5 (DSM 5), but it’s common.
The negative emotional reactions experienced by those suffering from misophonia can range from very mild irritation to a full-fledged fight reaction. This makes addressing misophonia not just about reducing discomfort but also about improving the overall quality of life through tailored therapeutic approaches.
Table of Contents
Misophonia Symptoms
Misophonia symptoms involve abnormal responses to specific triggers. These triggers range from person to person. A person may respond to a misophonia trigger without any visible external reaction, keeping their feelings and emotions contained internally. Others may find it much more challenging to control their feelings. This leads them to react by glaring, leaving the area, or sometimes responding with anger.
In extreme cases, the effects of misophonia can be debilitating! First, let us review the symptoms.
Emotional Responses
The emotional responses after hearing a triggering sound in misophonia are intense and can act quickly. What might start as simple annoyance can quickly escalate to severe anger or anxiety. These emotional responses are difficult to control, most likely the source of the triggering sound. For many people, their feelings can feel so poorly experienced that they are overwhelming, causing significant distress and difficulty in daily life.
Physical Responses
The physical reaction to a misophonia trigger is similar to what someone feels when experiencing fear or danger. A trigger can elicit a fight-or-flight response, which causes misophonia sufferers to experience physiological symptoms. It includes increased heart rate, blood pressure, goosebumps, tightness in the chest, and sweating.
These physiological symptoms heighten the distress with these sounds, making it more challenging for them to regulate their emotion and behavior.
Behavioral Responses
Behavioral responses to misophonia triggers can vary, but they are generally automatic, difficult to control, and have varying intensities. Most evidence suggests non-violent actions, like glaring, yelling, leaving, and avoiding specific people or situations.
There are very rare cases of violent outbursts against the source of the sound. Misophonia behavioral responses can still have damaging effects. It includes social withdrawal from people, ruining relationships, and disrupting everyday life, which can lead to isolation.
Misophonia Triggers
Misophonia triggers vary widely from person to person and may change over time. While some individuals may only react to a single specific trigger, others may have multiple triggers that provoke intense reactions. The individualized nature of triggers makes it difficult to define a fixed set that applies to everyone. However, several common triggers affect most individuals with misophonia.
Bodily sounds
Examples of common bodily sounds that trigger misophonia include eating, slurping, swallowing, lip-smacking, yawning, snoring, huffing, heavy or irregular breathing, throat-clearing, or sniffling.
Triggers usually feel more troublesome when the source is a nearby person rather than far away or as a result of an electronic device (TV, radio), where the source is unwittingly difficult to discern.
Non-bodily sounds
These trigger sounds might include tapping a pen, a ticking clock, slamming a door, typing, writing, or chirping birds.
Visual Triggers
Visual triggers, such as repetitive movements like twirling hair, wagging a foot, or rubbing one’s nose, can also provoke similar reactions.
How to Tell if You Have Misophonia
It is important to distinguish between sound sensitivity and misophonia when children are involved. Identifying the condition early can help with providing appropriate treatment and support.

Most people experience sound annoyance or irritation from time to time; however, it does not mean that they have misophonia. If you are able to recognize that you or someone else has misophonia, consider the following:
Intensity of Emotional Reaction
With misophonia, reactions to sound triggers often go beyond mild annoyance. Reactions may sometimes involve extreme feelings like panic, rage, or disgust, which feel overwhelming and uncontrollable.
Consistency of Triggers
Misophonia is distinct from other types of negative feelings that may sporadically and erratically occur. The same typical behaviors (chewing, tapping, clicking) always generate the same strong reaction in a person with misophonia.
Lack of Control
Many people with misophonia feel as if they have no control over their reactions to the displeasing sounds. This may escalate very quickly and feel very extreme compared to what happened.
Guilt After Reaction
Many individuals with misophonia feel sorry or guilty about how they acted after a displeasing sound. This often leads to self-blame, which creates an additional emotional distress.
Impact on Daily Life
The impact of misophonia is significant on daily life and relationships. If any of the signs described above are relevant to you, we would encourage you to seek professional help. The condition still has some way to go research-wise to enhance our therapeutic understanding of the condition and improve treatments that should alleviate people’s day-to-day suffering.
For example, the use of white noise generators, or immersive noise devices, shows promising results in managing reactions to triggers. If you are experiencing misophonia, there is help available. Effective treatments are available to improve your quality of life.
Who Does Misophonia Affect?
Misophonia affects about 1 in 5 people during their lifetime. Misophonia is more prevalent in women. In fact, studies have reported that women make up 55–83% of cases of misophonia. It can develop at any age, but it typically arises in early adolescence. How severely individuals experience misophonia can vary from person to person.
Possible Causes of Misophonia
While experts are still uncertain as to what causes misophonia, they have identified several possible influencing factors.
Differences in Brain Structure
Research has shown that neurological differences in the brain structures that control emotions and interpret sounds are important factors. These brain regions form the brain’s self-protection system. If there is an overactive self-protection system, the person may respond negatively, making the sound less tolerable.
Genetics
Some preliminary evidence indicates there may be a genetic cause to misophonia. One specific mutation may be linked to misophonia, but we do not yet know enough about the genetics involved.
Other Conditions
In addition to mental health and neurodevelopmental disorders like autism, ADHD, depression, OCD, PTSD, and borderline personality disorder, hearing-related disorders such as tinnitus and hyperacusis may also contribute.
Treating Misophonia
To officially diagnose misophonia, health professionals will generally ask a set of questions to elicit the person’s experiences and will recognize patterns and common features that confirm misophonia exists. After misophonia is diagnosed, the diagnosis is helpful to identify ways to address the symptoms.
Psychotherapy
Here are some psychotherapeutic techniques that can help improve misophonia symptoms:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a common technique that allows the patient to recognize how they respond to triggers and how they can develop techniques to cope. One of the aspects of CBT is recognizing the negative thought patterns and triggers and making plans to cut the triggers. For example, practicing impulse control for reactive tendencies and diminishing sensitivity to triggers can make an impact by using CBT.
Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT)
DBT is primarily used to deal with the emotional systematic approach to misophonia. It provides modules that include stress tolerance, emotional regulation, mindfulness, and interpersonal effectiveness. These approaches focus on how to identify and increase skills to manage extreme emotions, be present in the moment, stay present, and improve their social interactions.

Relaxation Exercises
These exercises are also helpful when diagnosed with misophonia. Basic techniques like deep breathing and progressive muscle relaxation help manage our physical reactions to triggers. Progressive muscle relaxation can help individuals go through tensing and relaxing different groups of muscles and can also teach them to relax when faced with triggers.
Other Techniques
Some providers use innovative methods and tools like biofeedback and hypnotherapy. Biofeedback uses sensors to control bodily response; hypnotherapy addresses subconscious triggers to lessen severity. These methods are promising, but additional research is needed to support their use in dealing with the symptoms of misophonia.
Noise Generation Devices
Not only will white noise help and be beneficial to people with misophonia but so too will pink noise and brown noise. All of these noises allow for a consistent background noise that masks triggering noises. For example, the sound of a river, waterfall, or rain. Examples of noise generation devices include ear-level devices. It includes small earphones with calming sounds combined with a background/white noise aspect, and room-level machines, such as white noise machine, fan, etc.
While there are many devices, a more economical option would be to use headphones connected to your phone. A variety of apps exist that generate white noise and other calming sounds.
Headphones that don’t fully block out external sounds can be ideal for adding background noise without creating complete isolation. You may also want to listen to other audio, such as music or podcasts, to help further engage your brain and divert your focus from the trigger. The goal is to address the discomfort you experience. For individuals that are dealing with intrusive thoughts, this is an effective approach to lessen the impact of the triggers.
Addressing Related Conditions
Misophonia is frequently associated with other conditions such as tinnitus (ringing in the ears) or mental health conditions such as anxiety, depression, or OCD. Treating these underlying conditions may provide some relief to misophonia symptoms. There is plenty of evidence that treating tinnitus, for example, can reduce the intensity and frequency of misophonia. Tinnitus Retraining Therapy (TRT) is a treatment aiming to help those with tinnitus increase their tolerance to noises and thus relieve misophonia symptoms.
Treating related mental health conditions – anxiety or OCD for instance—will also likely improve misophonia symptoms indirectly. These conditions are linked to escalating emotional responses to triggers. Treating them and working on reducing their intensity can allow someone with misophonia to experience a lesser intensity.
Additional Support and Adjustments
For individuals with misophonia, workplace accommodations or adjustments may be necessary to avoid triggers or manage their symptoms effectively. This could include changes to the work environment, such as noise-canceling headphones, designated quiet areas, or adjustments to work tasks that involve triggering sounds. Healthcare providers can offer guidance and resources for workplace accommodations.
Moreover, online support groups and social media communities provide valuable opportunities to connect with others experiencing misophonia. These platforms offer a sense of solidarity, where individuals can share strategies, ideas, and resources for coping with the condition.
Seek Help Today!
Misophonia is a complex and often misunderstood condition, but with the right strategies and treatments, individuals can manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Whether it’s through therapy, noise generation devices, or addressing related conditions, it’s important to seek the support you need and explore the best options for you. Remember, you’re not alone, and with the right resources, you can take control of your triggers and find relief.
Have a great idea? Let EvolveDash bring it to life! We specialize in empowering businesses with innovative digital solutions. We create custom mobile apps and build user-friendly websites, providing tailored solutions to meet your needs.
With over 100 satisfied clients and 450 successful projects, our team has the expertise needed to help your business stand out in a competitive market. Reach out to us today!
FAQs
What is misophonia?
Misophonia is a condition where certain sounds trigger intense emotional reactions like anxiety, anger, or even panic. Common triggers include sounds like chewing, sniffling, or tapping.
How is misophonia treated?
Treatment may involve therapies like CBT (Cognitive Behavioral Therapy), DBT (Dialectical Behavioral Therapy), relaxation exercises, and noise-generation devices. In some cases, addressing underlying conditions like anxiety or tinnitus can help reduce symptoms.
What are common triggers for misophonia?
Triggers can vary, but common ones include chewing, slurping, tapping, or sounds like a clock ticking. Visual triggers, such as twirling hair or foot tapping, can also be problematic.
Is misophonia linked to other conditions?
Yes, misophonia is often found alongside conditions like tinnitus, ADHD, OCD, and anxiety. Treating these related issues can sometimes improve misophonia symptoms.
Can misophonia be managed?
Yes, with proper treatment, including therapy, lifestyle changes, and noise-canceling tools, misophonia can be effectively managed.



















